Corn & Soybean Drought Update – 8/12/21
According to the USDA, the percentage of corn located within an area experiencing a drought declined to a nine week low level as of Aug 10th but remained at the highest seasonal level experienced throughout the past nine years. The percentage of soybeans within an area experiencing a drought also declined from the previous week, reaching a ten week low level but remaining at a nine year high seasonal level.
U.S. Drought Monitor:
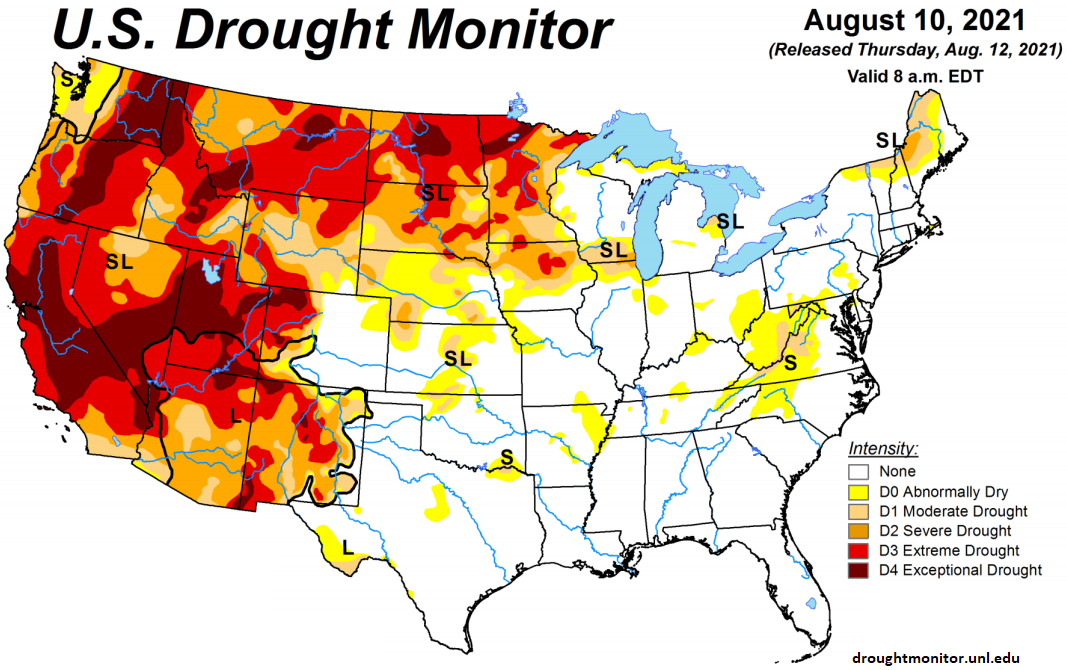
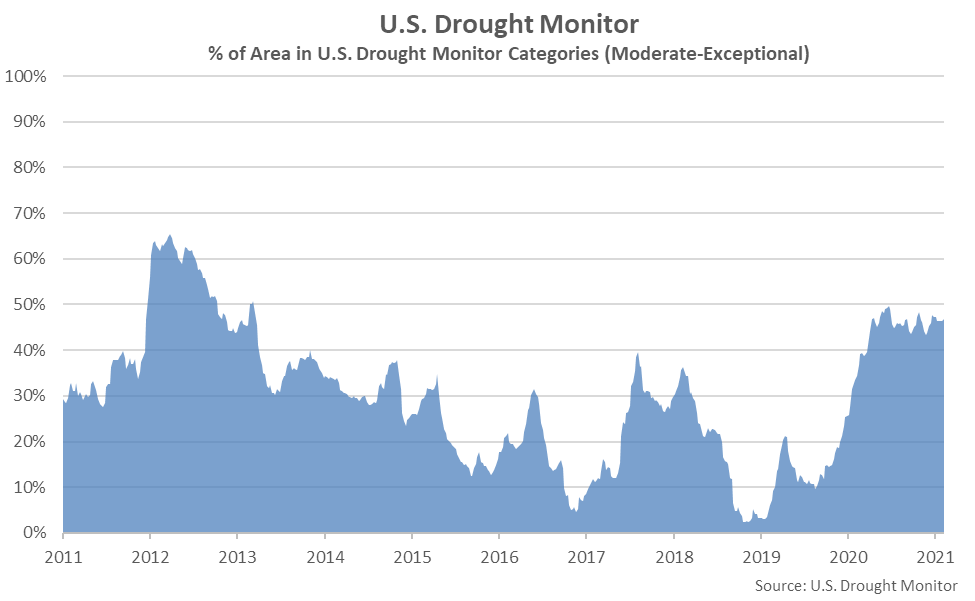
The U.S. Drought Monitor showed 47% of the continental U.S. being in a moderate-to-exceptional drought state as of Aug 10th, up one percent from the previous week and remaining at a nine year high seasonal level.
Corn:
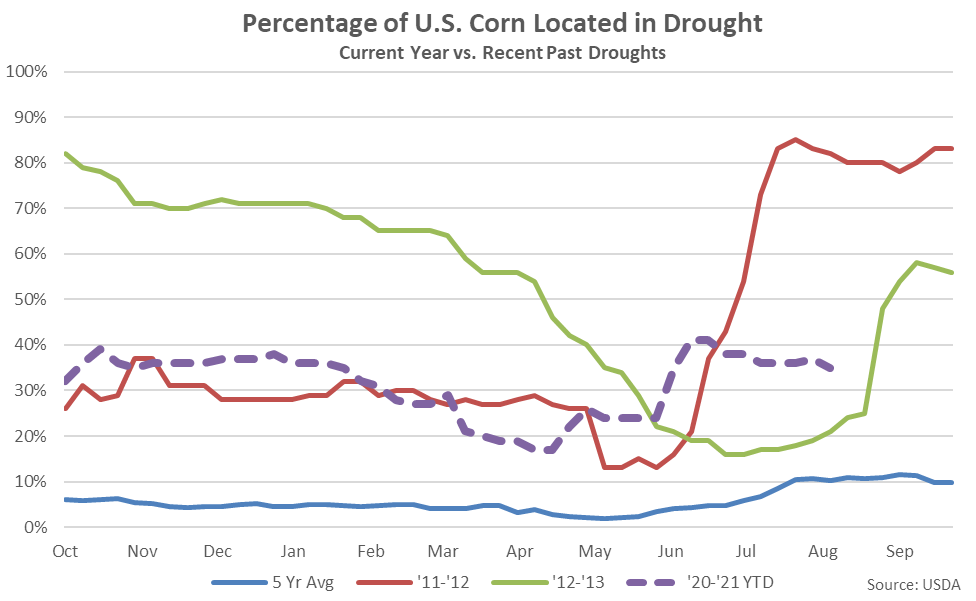
Approximately 35% of corn production was within an area experiencing a drought as of Aug 10th, down two percent from the previous week and reaching a nine week low level.
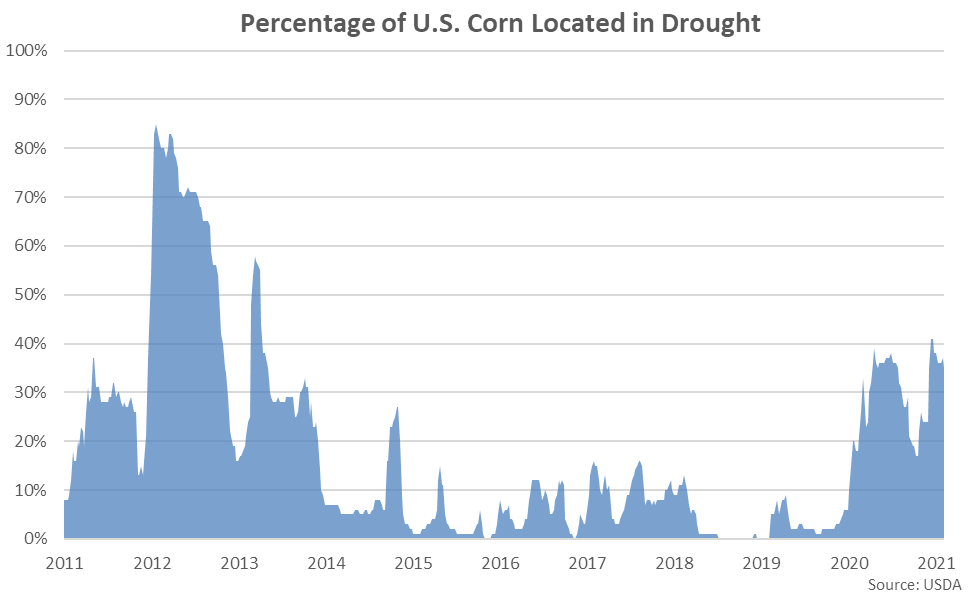
The percentage of U.S. corn located in a drought state remained at a nine year high seasonal level, finishing significantly above the five year average seasonal level of just ten percent. U.S. corn located in a drought state remained significantly below the 2012 seasonal level of 82%.
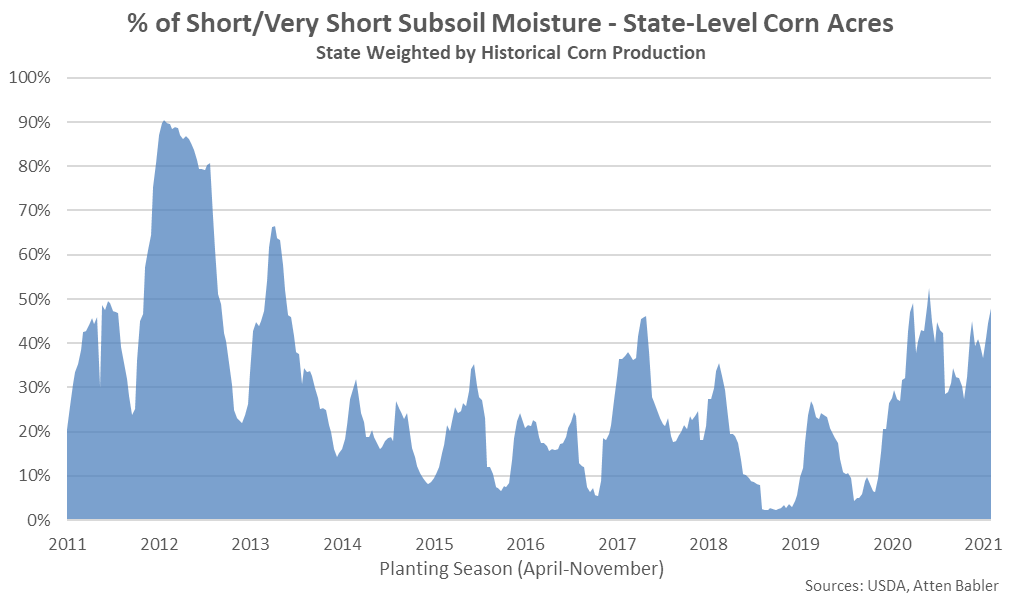
It is estimated that 48% of state-level corn acres had short-to-very short subsoil moisture as of the week ending Aug 8th, up three percent from the previous week and reaching a five month high level.
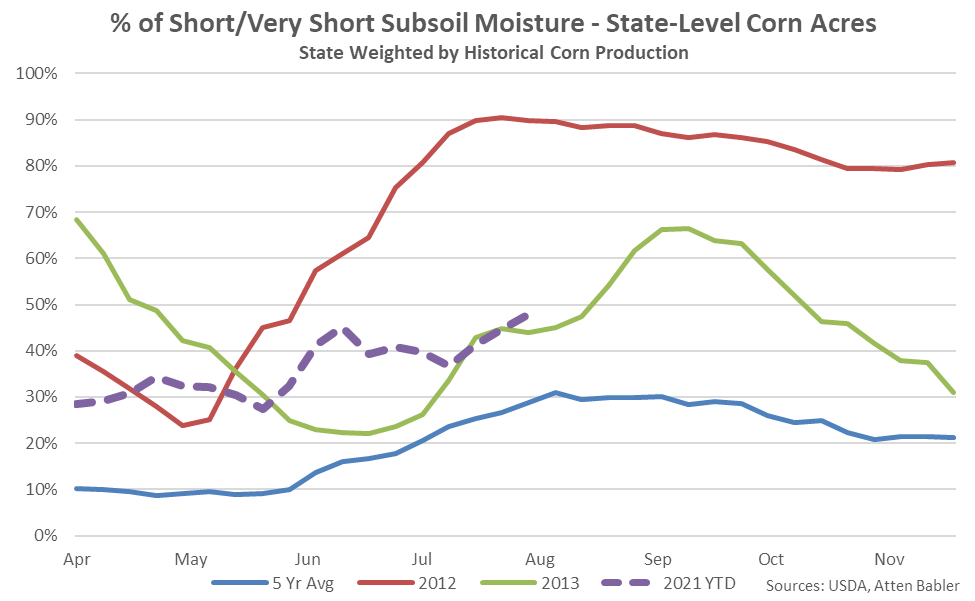
The percentage of U.S. corn with short-to-very short subsoil moisture reached a nine year high seasonal level as of the week ending Aug 8th but remained significantly below the 2012 seasonal level of 90%.
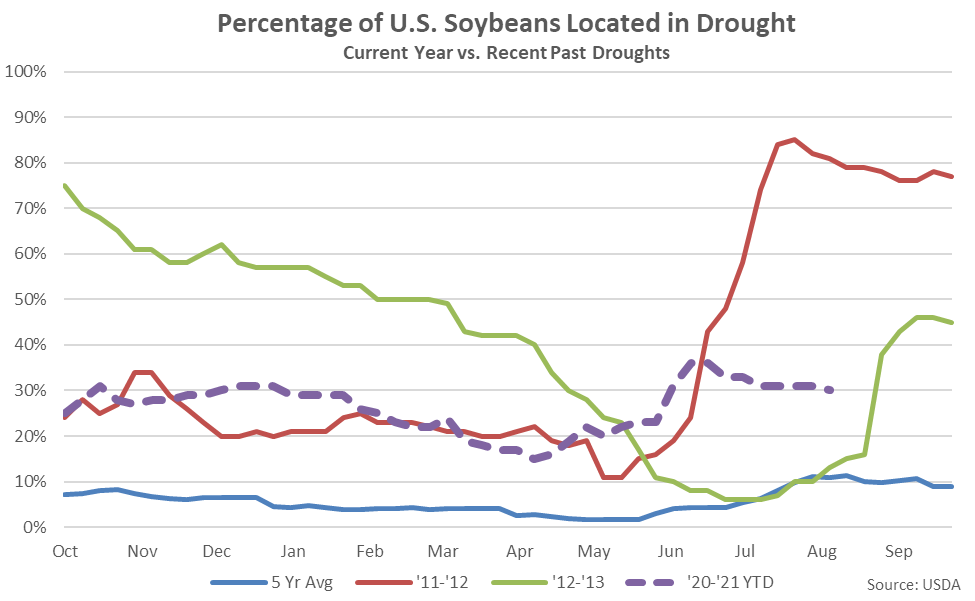
Soybeans:
Approximately 30% of soybean production was within an area experiencing a drought as of Aug 10th, down one percent from the previous week and reaching a ten week low level.
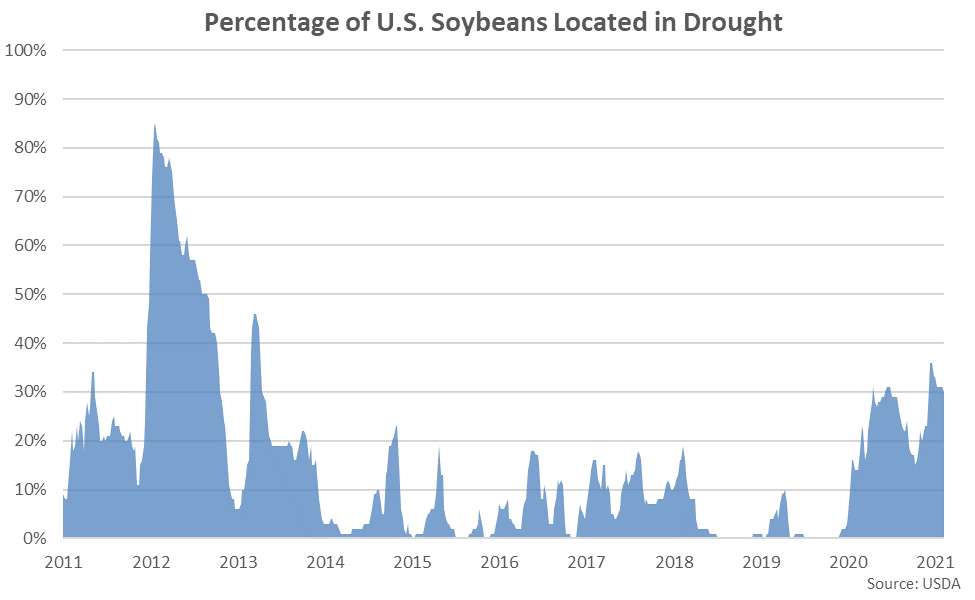
The percentage of U.S. soybeans located in a drought state remained at a nine year high seasonal level, finishing significantly above the five year average seasonal level of just 11%. U.S. soybeans located in a drought state remained significantly below the 2012 seasonal level of 81%.
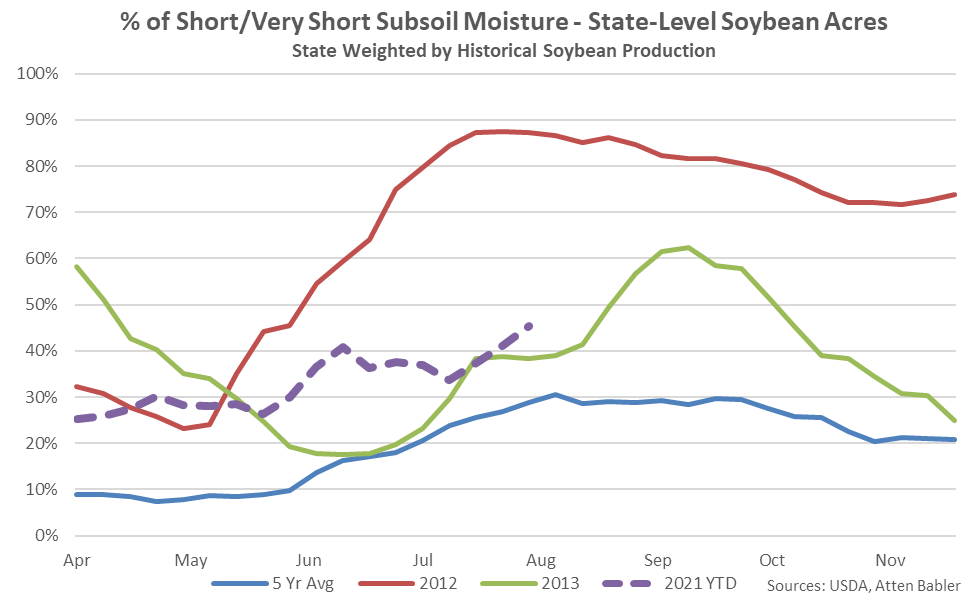
It is estimated that 45% of state-level soybean acres had short-to-very short subsoil moisture as of the week ending Aug 8th, up four percent from the previous week and reaching a five month high level.
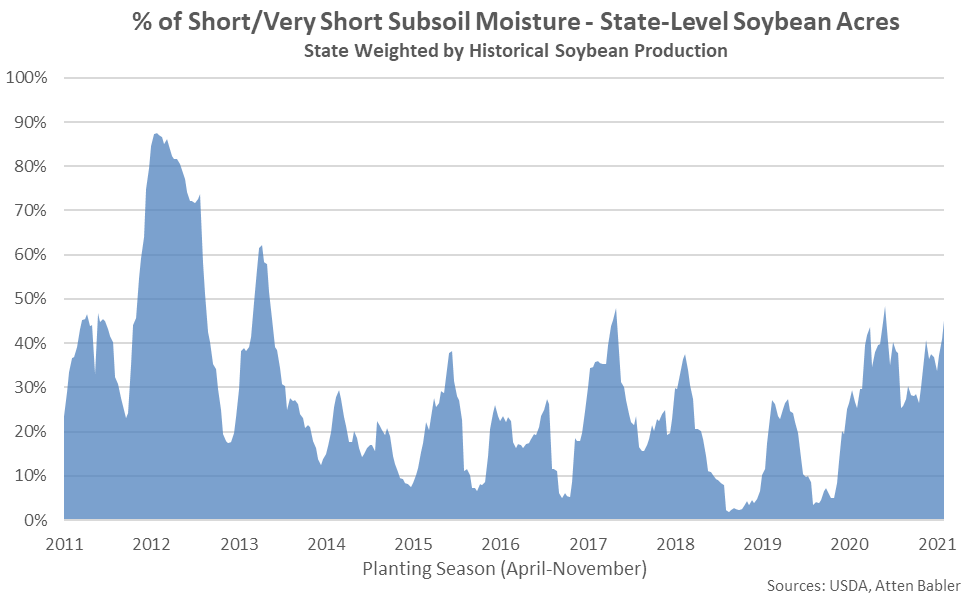
The percentage of U.S. soybeans with short-to-very short subsoil moisture reached a nine year high seasonal level as of the week ending Aug 8th but remained significantly below the 2012 seasonal level of 87%.